Application of KIC ultra-high speed and high-throughput cell analyzer in screening tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Vala Cell Imaging Analysis System Enables High-throughput Screening for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors That Cause Cardiotoxicity
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are potent anticancer drugs but have cardiovascular side effects, ranging from induced arrhythmias to heart failure.
To screen for TKIs with side effects, professors at the Tanford Cardiovascular Institute and the Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine Institute at Stanford University School of Medicine, through the use of 11 healthy individuals and 2 specific patients who received cancer treatment Induction of pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs) was performed using a KIC ultra-high-speed, high-throughput cell analyzer from Vala Science to measure changes in cardiomyocyte viability, contractility, and cell electrophysiology using patch clamps. Calcium treatment and signal testing, cardiotoxicity screening of FDA-approved TKIs, using KIC ultra-high-speed high-throughput cell analyzer to obtain key cell contraction data, confirmed that VEGFR2/PDGFR inhibitory TKIs can be induced at clinically relevant concentrations hiPSC-CMs produces cardiotoxicity and developed a "heart safety index" to assess the cardiotoxicity of existing TKIs and published the results in the journal Sci Transl Med (IF16.2) entitled: "High-Throughput Screening of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Cardiotoxicity with Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Specific experiment
To study the cardiotoxicity of FDA-approved TKIs to hiPSC-CMs, 11 healthy individuals and two individuals receiving TKIs for cancer treatment were recruited. Through a skin perforation biopsy or blood draw to obtain the main tissue sample that produces hiPSC: skin fibroblasts or peripheral hiPSC-CM, after which the cells are cultured in human albumin and ascorbic acid medium, this cardiomyocyte culture medium is deficient Growth factors such as insulin and IGF1; differentiated cells are glucose starved and need to be supplemented with 5 mM DL-sodium lactate for metabolically selecting hiPSC-CMs. The obtained pure hiPSC-CMs were seeded in a 384-well plate at a concentration of 25,000 cells/well, and treated with 0-100 μm TKIs for 72 hours, and cell viability was measured.

figure 1
Rapid determination of the shrinkage of hiPSC-CMs using the Vala KIC high-throughput cell analysis system
High-throughput cardiotoxicity screening of 21 small molecule TKIs was performed using hiPSC-CMs cells. Many TKIs inhibit multiple RTK families and induce cardiotoxicity including left ventricular dysfunction, myocardial infarction, or arrhythmias. However, the effects of cancer treatment outweigh these risks, and these drugs are often designated drugs at major cancer treatment centers. Highly cardiotoxic anthracyclines, doxorubicin as a positive control, use PROSTOBLAST cell viability assay to find VEGFR2/PDGFR inhibitory TKIs such as sorafenib, repaglinide, and enkephalin induced most hiPSC-CMs cells For death, the LD50 was 3.4 μm, 7.1 μm, and 4.3 μm, respectively (Fig. 2A). Doxorubicin is very toxic at 0.78 μM LD50. TKIs have no strong relationship with cytotoxicity. For example, the LD50 of imatinib and erlotinib are 78.20μm and 87.60μm, respectively, and Sola is confirmed by quantitative cell activity test. Fennis, regoravinib and ponatinib were highly cytotoxic to the 11 healthy control hiPSC-CM cell lines (Figures 2A-2C; Figure S3).
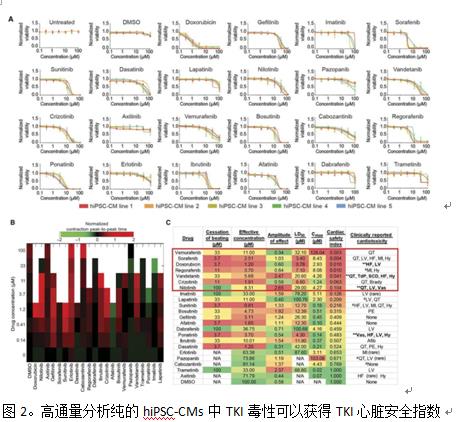
Cytotoxicity tests were also performed on human hiPSC CMS and hiPSC ECS from two patients with kidney cancer. These patients received two TKIs: sunitinib as first-line therapy and axitinib as second-line therapy. These patients were found to have no significant clinical cardiotoxicity to any TKIs. As expected, no significant differences in cytotoxicity after administration of sunitinib or axitinib were observed in patients receiving TKI and hiPSC-CM and healthy controls hiPSC-CM.
To avoid lab-to-experimental deviations and changes in the quality of hiPSC-CM, we treated the commercial healthy hiPSC-CMS with TKIs for 72 hours, followed by Hoechst 33258 (Life Technologies, H3569) and Alexa-Fluor 488 markers. The cells were subjected to contraction evaluation of cells in 384-well plates by sequence analysis of the cells of the 384-well plate by a KIC200 dynamic imaging cytometer of Vala Sciences at a imaging speed of 100 Hz for a period of 6.5 seconds. Cells treated with TKIs such as nilotinib and valdecanib were observed, and at a dose lower than the LD50 cytotoxicity value, the hiPSC-CM beat rate and other parameters were changed, and irregularities were found before myocardial cell death. Beat (Figure 2B, Figure 5). Changes in the hiPSC-CM contractility parameter after increasing the TKI concentration, the effective drug concentration at which initial contractile force change occurred, and the TKI concentration at which hiPSC-CM cells stopped contracting were also measured (Fig. 2C, Fig. 56, Fig. 7). To accurately assess the toxicity of TKIs, and to examine the concentration of toxic TKIs, it was observed whether the cytotoxicity and contractility were matched to the patient experience dose using the Vala KIC system . The patient Cmax value was obtained from the FDA literature as an estimate of the patient's TKI plasma concentration (Fig. 2C). By homogenizing the effective concentration of extracorporeal arrest and LD50 cytotoxicity data with the Cmax values ​​reported in the literature, we developed a "heart safety index," a TKI measure that identifies clinical cardiotoxicity (Figure 2C, Figure 7). Three-sevenths of the drugs had a cardiac safety index of 0.10 or lower (doxorubicin, nilotinib, and vandetanib), which was previously labeled by the FDA as a black box heart toxicity warning. A safety index value of 0.10 was chosen as the threshold for high cardiotoxic drugs as a clinical cardiotoxic drug and black box drugs (doxorubicin, nilotinib and vannadanib) and other compounds not associated with cardiotoxicity. The safety index demarcation point between. Two black box-type TKIs, nilotinib and vantanitani, caused QT interval prolongation and arrhythmia and were selected for further analysis. Three TKIS with a safety index below 0.10 are VEGFR2/PDGFR inhibitory TKIs (Rigranable, Sorafenib and Mannapini). Regvavir and sorafenib have safety targets comparable to cardiotoxic anthracyclines. These statistics from the VALA KIC200 cell analyzer indicate that VEGFR2/PDGFR inhibitory TKIs induce cardiotoxicity in hiPSC-CMs at clinically relevant concentrations, comparable to the dose experienced by patients. Clinically, VEGFR2/PDGFR inhibitory TKIs can cause a variety of cardiovascular toxicity, including hypertension, heart failure, and QT prolongation.

It was also determined by phosphoprotein analysis that VEGFR2/PDGFR inhibitory TKI resulted in a compensatory increase in protective insulin and insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling in hiPSC-CMs. Cardiac protection signals up-regulate exogenous insulin or IGF1, improving the viability of hiPSC-CMs in myocarditis VEGFR2/PDGFR synergistic inhibitory TKIs.
Therefore, data from the VALA KIC high-throughput cell analyzer also confirmed that hiPSC-CMs can be used to screen for cardiovascular toxicity associated with anti-cancer TKI and correlate with clinical phenotype. This approach provides unexpected insights and toxicity can be alleviated by cardiac protective insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling.

Advantages of VAlA KIC Real-Time Ultra-High Speed ​​Cell Analysis System for Cell Cardiotoxic Drug Screening:
★ Ultra-high imaging speed: 0.1-1500Hze, suitable for cell contraction and jitter analysis
★Single cell analysis: real-time first single field or multiple fields of each cell
★Double focus imaging: surface tracking + image focusing to ensure clear image of each cell
★High throughput: 96/384-well high-throughput analysis, the fastest 1-2min/96 holes
★ Standard 4 fluorescent channel and dual objective lens, channel and objective lens can be expanded
Tetanus Shot,Tetanus Vaccine,Hepatitis B Injection,Hep B Vaccine
FOSHAN PHARMA CO., LTD. , https://www.fspharmamedicine.com